Hernias are a common problem that result in a bulge in the stomach or groin. There are many types of hernias. They can hurt you, but most of the time, you only see swelling or lumps in your stomach or groin. And they usually don’t leave without treatment, which often means surgery. Often harmless and painless, but sometimes it can cause discomfort and pain.
In this article, Dr Venu Gopal Pareek explains what are hernias, types of hernia, cause, symptoms, and how to treat them.
What is Hernia?

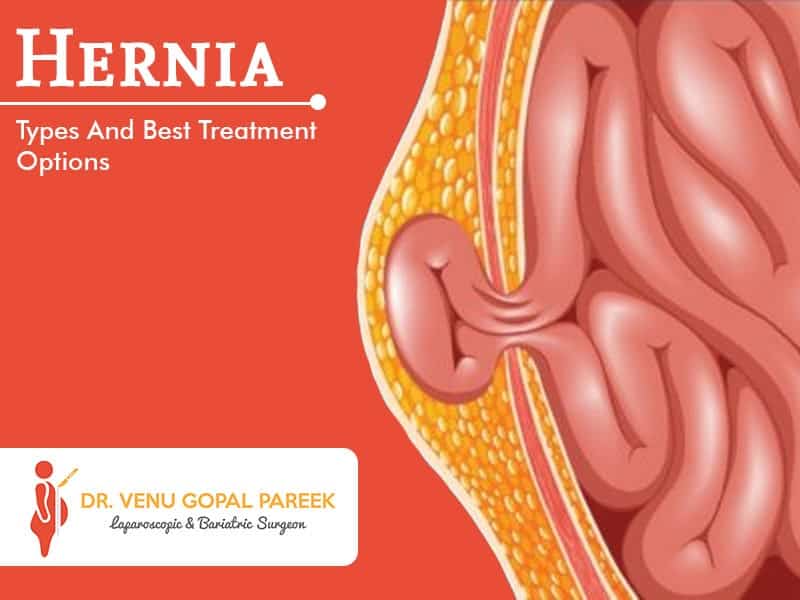
Hernias occur when the internal organs of the abdominal cavity protrude around the muscle wall that usually holds it in place. Some of the leading causes of hernias are tobacco or smoking, malnutrition, chronic constipation, etc. Hernias can appear on the stomach, thighs, abdomen or groin.
What Causes Hernias?

Different types of hernias can have different causes. Generally, hernias begin with pressure on your organs or intestines. Hernias occur when this pressure occurs in the same area as weakened muscle or tissue. Some people are born with weak muscles or tissues that do not develop fully. However, most people suffer from hernias when their bodies age and their muscles weaken.
You can also get hernias from specific movements and habits, or make existing hernias worse. This includes:
- Lifting heavy objects (mainly due to incorrect lifting and muscle weakness)
- Excessive use of the same muscle
- Strained movements (e.g. persistent coughing, sneezing, diarrhoea or constipation)
- Being overweight or eating poorly
- Usage of Tobacco
What Are The Symptoms Of A Hernia?

In many cases, it is only painless swelling that does not cause problems and does not require immediate medical attention. However, discomfort and pain can occur when performing certain activities, e.g. lifting. In some cases, for example, if the intestine suffers from a hernia, immediate medical treatment or even hernia surgery may be needed. Other symptoms that may require treatment for a hernia are as follows:
Reducible Hernia:
It can be a new lump in the groin or the stomach
- Can hurt, but not soft to the touch
- Pain precedes in the lump area
- Bumps can increase in size when standing or coughing continuously or sneezing
- It can be pushed back unless very large
Irreducible Hernia:
- Sometimes painful
- Enlargement of the hernia that previously reduced
- It can be chronic without pain
- It is also known as an incarcerated Hernia
- It leads to strangulation of the hernia
- Symptoms of intestinal obstruction can include such as nausea and vomiting
Strangulated Hernia:
- Blood supply to the closed intestine is cut off
- Pain followed by tenderness
- Nausea and vomiting
- The person can look sick with or without fever
Types Of Hernia:

Common types of hernia are as below:
- Inguinal Hernia: These hernias make-up seventy-five percent of all hernias in the abdominal wall and are more common in men than in women. These hernias are divided into two types, direct and indirect. Both occur in the groin area, where the skin of the thigh connects to the body. Both hernias will appear as a bulge in the groin area. The difference between direct and indirect hernias, however, is an essential part of clinical diagnosis.
-
- Indirect inguinal Hernia: Inguinal hernias indirectly follow the path that the testicles cover from the stomach to the scrotum during fetal development. At this time it closes indefinitely before birth but can be a place for inguinal hernias later on. Sometimes a hernia sac can protrude into the scrotum. Indirect Inguinal hernias can occur at any age.
- Direct inguinal Hernia: Direct inguinal hernias occur in a separate area where the abdominal wall is slightly thinner. It will rarely protrude into the scrotum and can cause pain which, apart from testicular pain, is difficult to understand. In contrast to indirect hernias, which can occur at any age, direct hernias occur in adults because the abdominal wall becomes weaker with age.
- Incisional Hernia: These hernias appear at the site of previous abdominal surgery where the intestine pushes against the abdominal wall. It often occurs in overweight people or inactive people, especially after stomach surgery.
- Femoral Hernia: The femoral canal is the path through which the femoral arteries, veins and nerves exit the abdominal cavity to enter the thigh. Although it is usually a stiff space, it often becomes so large that the contents of the stomach (usually the intestine) extend into the canal. Femoral hernias cause a bulge just below the groin, roughly in the middle of the upper leg.
Femoral hernias often occur in women and are especially at risk of being irreversible (irrevocable) and suffocation (impaired blood supply). Not all irreversible hernias get strangled (the blood supply is interrupted), but a qualified doctor must examine all irreversible hernias.
- Umbilical Hernia: This common hernia (10% -30%) often occurs in children at birth and is considered to have a distended stomach (navel). Umbilical hernias occur when a hole in the child’s abdominal wall, which usually closes before birth, is not entirely closed. When this type of hernia is small (less than half an inch), it usually closes when you are two years old.
Larger and non-closed hernias require surgery when the child is 2 to 4 years old. Even if the area closes at birth, umbilical hernias can occur later because this place can remain a weak spot in the abdominal wall. Umbilical hernias can occur then in life or pregnant or born women, caused by additional stress in the region. They usually do not cause stomach pain.
- Hiatal Hernia: This type of hernia occurs when the abdomen pushes through the diaphragm. The diaphragm usually contains a small gap in the oesophagus. This gap gets cured when the stomach is pushed out. Small hyaline hernias may not cause significant symptoms, but larger ones can cause pain and heartburn.
Rare Types Of Hernias:
- Diaphragmatic Hernia: This is usually a congenital abnormality that causes the opening of the diaphragm through which the contents of the stomach enter the chest cavity.
- Spigelian Hernia: This rare hernia occurs when the rectus abdomen muscles are through the Spigelian connective tissue a few centimetres from the middle of the stomach.
- Obturator Hernia: This very rare abdominal hernia mainly occurs in women. This hernia protrudes from the cavity through a gap in the hip bone. It does not show bulges, but can act as intestinal obstruction and cause nausea and vomiting. They are complicated to diagnose this hernia because of the lack of visible protrusions.
- Epigastric Hernia: Occur between the navel and thus the structure of the lower skeleton of the abdominal sheet. It usually consists of adipose tissue and rarely contain intestine. These hernias form in relatively weak areas of the abdominal wall and are often painless.
When To See A Doctor:
Consult a doctor in the following cases:
- The bulge becomes painful.
- Vomiting occurs, accompanied by protrusions.
- Bulges swell more or change colour.
Consult a Dr Venu Gopal Pareek in Hyderabad for permanent treatment of hernias.
How Are Hernias Diagnosed?

To diagnose your condition, your doctor will first do a physical examination. During this examination, your doctor may feel swelling in the abdomen or groin that increases when you sit, cough, or feel tense. Your doctor will then record your medical history. Your doctor will also likely use imaging tests to diagnose them. They are:
- Abdominal ultrasound
- CT scan
- MRI scan
- Barium X-ray
- Endoscopy
Treatment Of Hernia:
The need to treat hernias depends on the size and severity of symptoms. Hernia treatment includes three choices:
- Lifestyle changes
- Medication
- Surgery
Lifestyle Changes:
Changes in eating patterns can often cure symptoms of Hiatal hernias, but do not make the hernia cure completely. The person concerned is asked to avoid large or heavy meals and not to bend or lie down after eating. The person must maintain a healthy body weight.
Specific hernia exercises can help strengthen muscles at the location of the hernia, reducing symptoms. But if the activity performed incorrectly, the pressure in the area increases and the hernia swells. Therefore you need to follow the hernia or physiotherapist’s instructions correctly.
Hernia symptoms can get treated by avoiding foods such as spicy foods that can cause acid reflux or heartburn. Also, you can prevent acid reflux by losing weight and avoiding cigarettes.
Surgery:
Surgery to restore a hernia is performed to relieve pain, strengthen a weak muscle area, or return the abdominal organs into place. It can perform in two ways:
Traditional “Open” Surgery: Performed under local or general anaesthesia with a large incision, the surgeon pushes the organs back into the stomach. It uses to close the inguinal hernia with a mesh, thread, or both, and the wound closes with clips or surgical glue.

Laparoscopic Procedure:

- Surgeons highly recommend this surgical procedure. In laparoscopy, a thin telescopic instrument inserted through a small incision in the navel. The operation is done under general anaesthesia so you cannot feel pain during the procedure. Gas is used to inflate your stomach to make internal organs more visible.
- A tube is installed in one section and equipped with a mini camera (laparoscope). The surgeon uses a camera to insert small tools through other pieces to repair the hernia using synthetic mesh.
- People who have laparoscopic repair can experience slight discomfort and scarring after surgery and can return to normal activities more quickly. However, recurrence of a hernia is more likely to occur with laparoscopic recovery compared to open surgery. A surgeon experienced in laparoscopy can reduce this risk.
- Laparoscopy allows the surgeon to avoid scarring from previous hernia repair. Therefore, this is an excellent choice for people whose hernias appear after open hernia surgery. It can also be the right choice for people with hernias on both sides of the body (bilaterally).
- Compared with open surgery, it can take a few weeks for you to return to your normal level of activity. However, not all hernias are suitable for laparoscopic repair. It is especially true for hernias where a small portion of your intestine has entered the scrotum.
Conclusion:
If you suffer from hernias, it is best to discuss the exercise with your doctor or physiotherapist. They can work with you to tell you which exercises are good and how to do them properly to prevent irritation of your hernias.
Most types of hernias can be treated and repaired. However, hernias usually return. In some cases, surgery can help reduce this hernia. Talk to a surgeon about the best treatment options for you and how to prevent recurrence of hernias.
People with congenital diaphragmatic hernias can have other health problems. Talk to a doctor about how to treat and handle it. You need to realize that fear of surgery is normal. If your health condition does not require this, a doctor will not recommend it.
However, if you have questions about your operation, you can meet Dr Venu Gopal Pareek and have the best treatment for a hernia, which can help to reduce unnecessary stress. Contact Dr Venu Gopal Pareek at +91 91-777-77715.